Architecture can have a positive or negative impact on a building’s energy efficiency. But can it effectively improve air quality?
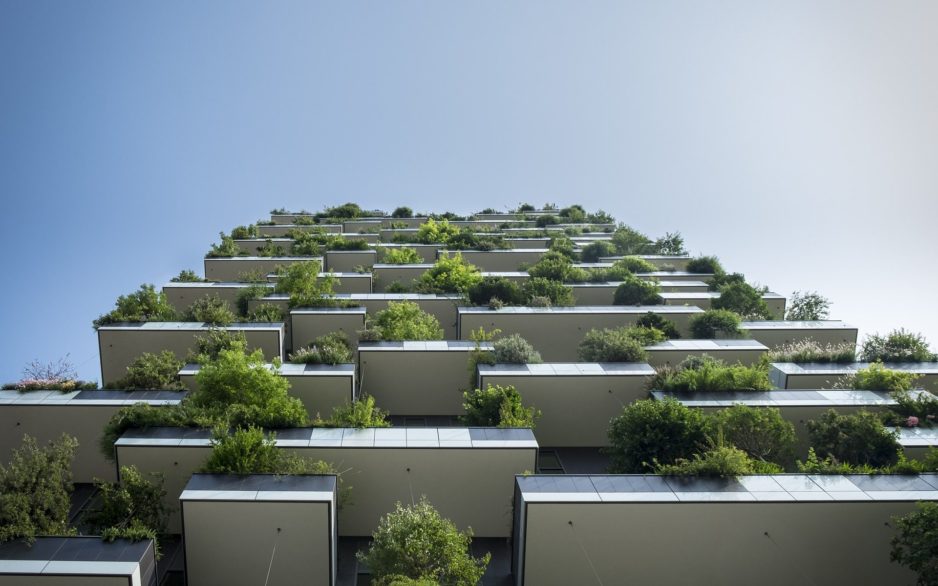
China started recently the construction of Liuzhou Forest City, which is expected to be a satellite neighborhood completed by 2020 connected to the main city by rail. It is a wild reminder of the importance of architecture in controlling air quality in our living environments. This city is specifically designed to fight air pollution by extensive use of vegetation throughout the building façade. The design by Stefano Boeri Architetti follows the experience of their two buildings inaugurated in Milan 2014: Bosco Verticale. In China, 1 million plants and 40,000 trees planted all over the project will absorb 1,000 tons of carbon dioxide and 57 tons of other pollutants per year.
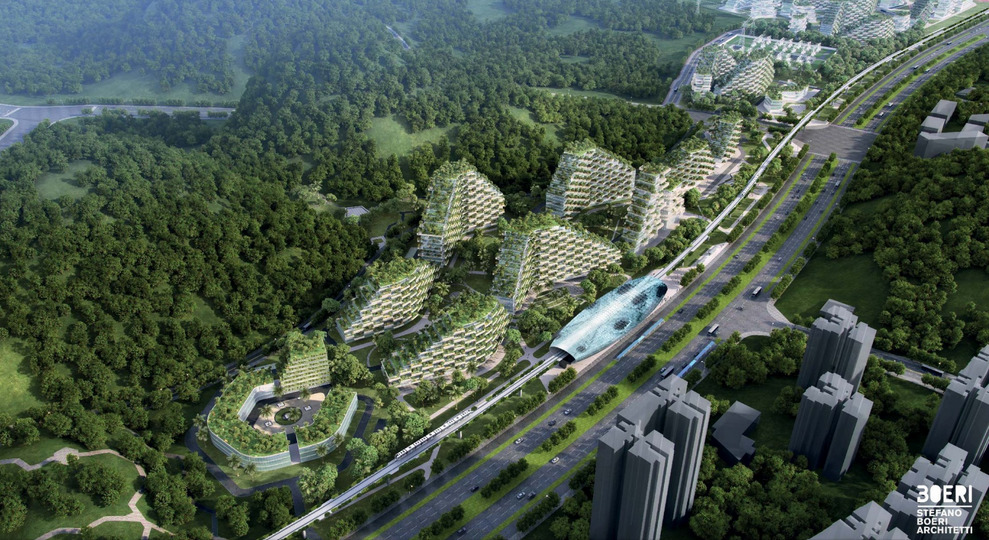

According to the architecture firm: “The diffusion of plants, not only in the parks and gardens or along the streets, but also over building facades, will allow the energy self-sufficient city to contribute to improve the air quality (absorbing both CO2 and fine dust of 57 tons per year), to decrease the average air temperature, to create noise barriers and to improve the biodiversity of living species, generating the habitat for birds, insects and small animals that inhabit the Liuzhou territory,”


The idea to control air quality through architecture is not new. For decades, urban planners have worked and invested in bicycle paths, innovative transportation programmes, and looked into how to improve the cities’ walkability. All features with the objective of reducing emissions from cars and transportation. However, the role of the physical buildings themselves in improving air quality is picking up with many novel ideas in the past decades.
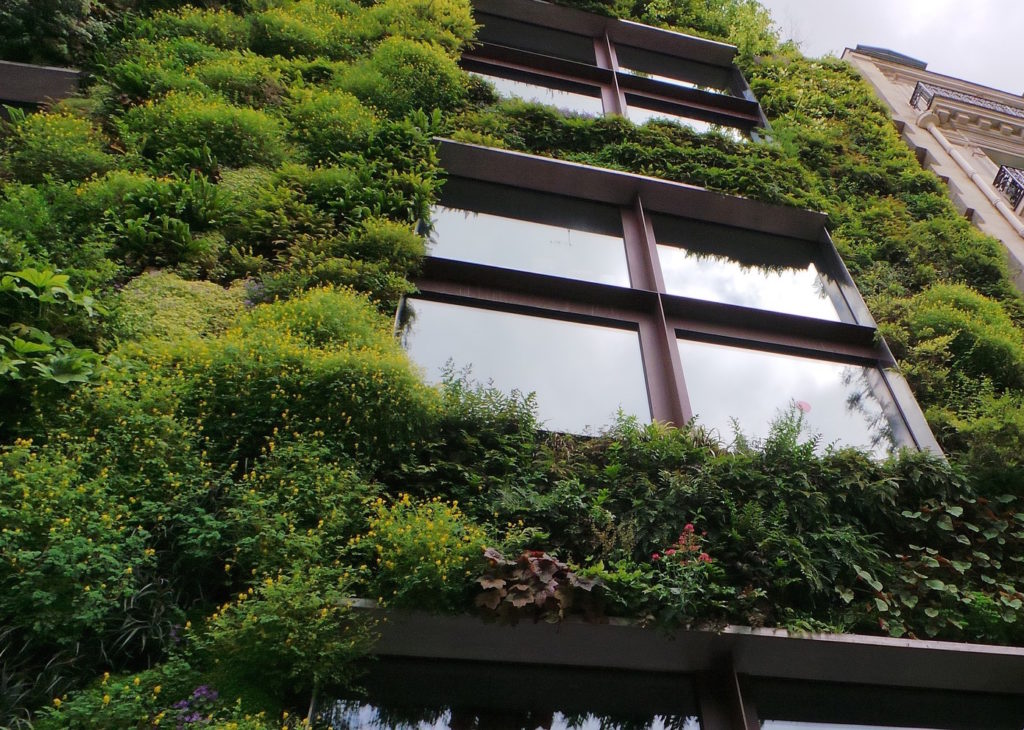
A few interesting and encouraging examples out there include 1. Mexico City, the Manuel Gea Gonzalez Hospital has an external structure that is coated with titanium dioxide. This coating -Provolste360e- helps break down pollutants when exposed to light by releasing free-radicals. Tiles coated with this substance can be used on any surface in the city and repurpose old façades. 2. Paris where the Musee Quay Branly with its living wall that absorbs carbon dioxide and emits oxygen. Yet another example is the Congress Gateway Towers in Chicago, which have an air filtration system to absorb CO2, which then feeds growing algae and is processed into biofuels to provide clean energy for the building.



There are also some smaller initiatives as standalone solutions: the Dan Rosengaarde Smog Free Tower, a smog sucking vacuum tower already installed in Beijing; and CityTree, the ultra tech green wall that can be displayed as urban furniture to help control air pollution.
Architecture has a lot to offer to control air quality, and ideas are sprouting in many directions.
They key to their use on a larger scale is to show their effectiveness by monitoring how air quality is improved following these various initiatives.