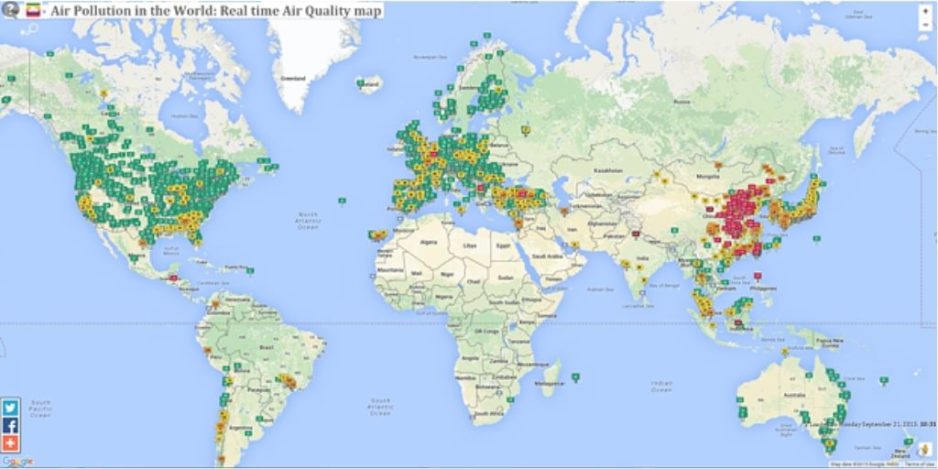
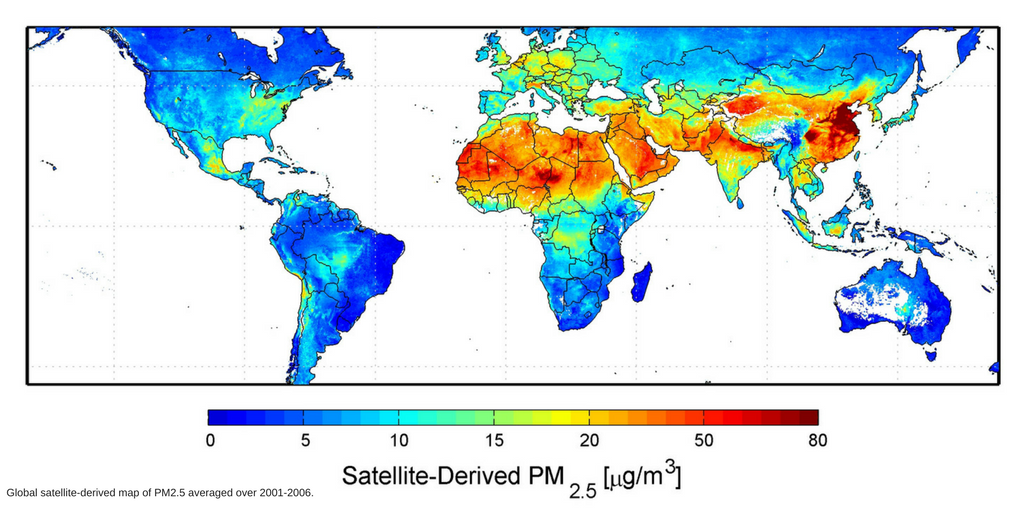
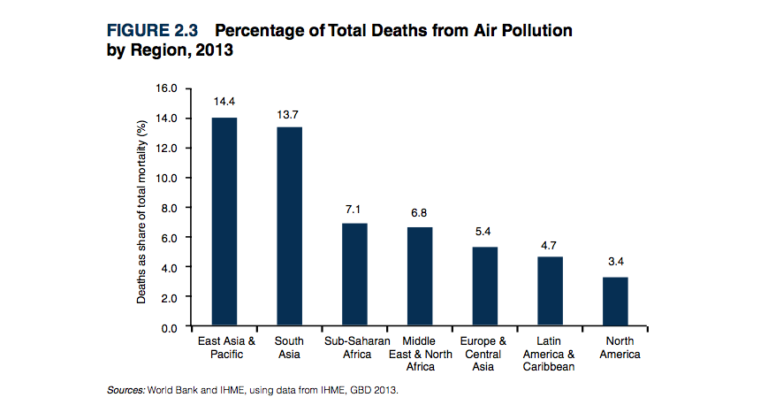
Air pollution is becoming more and more present in the news, in casual conversations, in the promotion of products and in many more instances. However, are we all talking about the same thing? What exactly is it that we all call ‘air pollution’?
Air pollution is a mix of natural and man-made substances in the air we breathe which is harmful to our health, it can be any physical, chemical or biological agent that modifies the natural atmosphere. Most sources of air pollution are man-made from mobile sources such as fuel powered motor vehicles; and stationary sources such as factories, refineries, power plants and forest fires. There are also other indoor sources such as building materials and cleaning products. Air pollution, as we now know is present both outdoor and indoor.
Outdoor air pollution:
- Fine particles (burning of fossil fuels in energy production, coal and petroleum used in vehicles)
- Gases (sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, chemical vapours and others)
- Ground-level ozone (smog)
Indoor air pollution:
Gases emanating from:
- Household products and chemicals, or
- Building materials such as paint, wood, furniture (asbestos, formaldehyde, lead etc)
- Allergens such as coackroaches, mold, pollen
The World Health Organization (WHO) in 2005 issued the ‘WHO Air Quality Guidelines’ to offer guidance and limits for the most worrying air pollutants because of their threat to human health, their widespread presence in urban areas and their relevance as precursors for other toxic components: particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulphur dioxide (SO2).
Particulate Matter
Is a mix of solid and liquid (organic or inorganic) particles suspended in the air. It is the pollutant that affects most people and is generally composed by sulphate, nitrates, ammonia, sodium chloride, black carbon, mineral dust and water.
Ozone (O3)
Ground-level Ozone is a major component of smog, formed by the reaction of sunlight with nitrogen oxides (NOX) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
NO2 is mostly the result of emissions during the combustion process (power generation, heating and engines). It is in fact, a source of nitrate aerosols that form PM2.5.
Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
SO2 is produced from fossil fuel burning for domestic use, power generation or motor vehicles
Other components generally referred to when talking about air pollution are carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which has greater relevance when talking about indoor air pollution, although also present outdoors.
VOCs are a collection of toxic gases from solids or liquids, that are found in higher concentrations indoors (up to ten times higher). Thousands of products used indoors as construction materials, paints, varnishes, cleaning agents, activities like cooking and many more, are the source of VOCs while being used and while stored. (6) Safe levels / guidelines for exposure to VOCs are not known,, but common sense rules are that they should be kept at low levels to avoid or reduce their negative health effects, which have been well documented.
CO and CO2 are not considered as VOCs. They are both odorless, tasteless and harmful to human health but have clear differences – CO2 occurs naturally in the atmosphere and we can tolerate it in small amounts, whereas CO can cause problems even in low concentrations and is flammable.
WHO AIR QUALITY GUIDELINES
- PM5
10 μg/m3 annual mean
25 μg/m3 24-hour mean - PM10
20 μg/m3 annual mean
50 μg/m3 24-hour mean - NO2
40 μg/m3 annual mean
200 μg/m3 1-hour mean - SO2
20 μg/m3 24-hour mean
500 μg/m3 10-minute mean - O3
100 μg/m3 8-hour meanWHO issued these guidelines as a global standard for environmental quality. Each country can adopt the guideline at its maximum standard or take interim standards that better reflect their national balance between health risks, economic decisions, technological capacities and other political and social factors.
Sources:
NIH – Air Pollution and Your Health
EPA – Pollutants and Sources
WHO – Air Pollution
WHO – WHO Challenges World to Improve Air Quality
WHO – WHO Guideline for Particulate Matter, Sulphur, Ozone…
EPA – Volatile Organic Compounds’ Impact on Indoor Air Quality